반응형
01. 리눅스/유닉스 시스템 프로그래밍이란
- 시스템에서 제공하는 시스템 콜을 이용해 프로그램 작성하기
-대다수 시스템 프로그래밍은 리눅스 기반으로 진행됨
02. 리눅스/ 유닉스 시스템 표준
- POSIX라는 유닉스 기반 인터페이스에 대한 이해 필요
- ANSI C 표준을 준수해야 한다
- 리눅스에서 안드로이드 등 우리가 일반적으로 많이 쓰는 운영체제들도 많이 파생되었다.

03. 시스템 프로그래밍
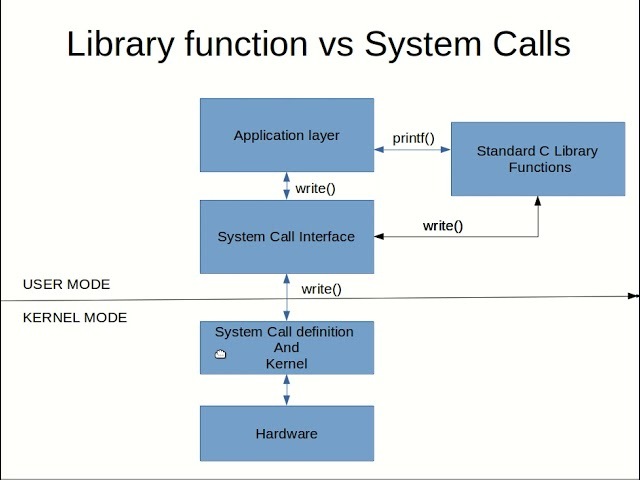
- 시스템 호출과 C언어 라이브러리는 실행 과정이 다르다.
- man 명령어를 통해 각 함수가 시스템 호출인지 라이브러리 함수인지 알 수 있다.
- 명령어에 대한 설명은 1번, 시스템 호출은 2번, 라이브러리 함수는 3번 섹션에 위치하고 있다.
- errno-base.h에서 오류 코드 확인할 수 있다.
#ifndef _ASM_GENERIC_ERRNO_BASE_H
#define _ASM_GENERIC_ERRNO_BASE_H
#define EPERM 1 /* Operation not permitted */
#define ENOENT 2 /* No such file or directory */
#define ESRCH 3 /* No such process */
#define EINTR 4 /* Interrupted system call */
#define EIO 5 /* I/O error */
#define ENXIO 6 /* No such device or address */
#define E2BIG 7 /* Argument list too long */
#define ENOEXEC 8 /* Exec format error */
#define EBADF 9 /* Bad file number */
#define ECHILD 10 /* No child processes */
#define EAGAIN 11 /* Try again */
#define ENOMEM 12 /* Out of memory */
#define EACCES 13 /* Permission denied */
#define EFAULT 14 /* Bad address */
#define ENOTBLK 15 /* Block device required */
#define EBUSY 16 /* Device or resource busy */
#define EEXIST 17 /* File exists */
#define EXDEV 18 /* Cross-device link */
#define ENODEV 19 /* No such device */
#define ENOTDIR 20 /* Not a directory */
#define EISDIR 21 /* Is a directory */
#define EINVAL 22 /* Invalid argument */
#define ENFILE 23 /* File table overflow */
#define EMFILE 24 /* Too many open files */
#define ENOTTY 25 /* Not a typewriter */
#define ETXTBSY 26 /* Text file busy */
#define EFBIG 27 /* File too large */
#define ENOSPC 28 /* No space left on device */
#define ESPIPE 29 /* Illegal seek */
#define EROFS 30 /* Read-only file system */
#define EMLINK 31 /* Too many links */
#define EPIPE 32 /* Broken pipe */
#define EDOM 33 /* Math argument out of domain of func */
#define ERANGE 34 /* Math result not representable */
#endif
04. 시스템 도구
- vi test.c 등으로 파일 열람 가능
- makefile로 여러 파일을 한꺼번에 컴파일 가능
-오류 메시지 출력: perror(3)
PERROR(3) Linux Programmer's Manual PERROR(3)
NAME
perror - print a system error message
SYNOPSIS
#include <stdio.h>
void perror(const char *s);
#include <errno.h>
const char * const sys_errlist[];
int sys_nerr;
int errno; /* Not really declared this way; see errno(3) */
Feature Test Macro Requirements for glibc (see feature_test_macros(7)):
sys_errlist, sys_nerr:
From glibc 2.19 to 2.31:
_DEFAULT_SOURCE
Glibc 2.19 and earlier:
_BSD_SOURCE
- 오류 메시지 출력: stderror(3)
STRERROR(3) Linux Programmer's Manual STRERROR(3)
NAME
strerror, strerrorname_np, strerrordesc_np, strerror_r, strerror_l - return string describing error number
SYNOPSIS
#include <string.h>
char *strerror(int errnum);
const char *strerrorname_np(int errnum);
const char *strerrordesc_np(int errnum);
int strerror_r(int errnum, char *buf, size_t buflen);
/* XSI-compliant */
char *strerror_r(int errnum, char *buf, size_t buflen);
/* GNU-specific */
char *strerror_l(int errnum, locale_t locale);
Feature Test Macro Requirements for glibc (see feature_test_macros(7)):
strerrorname_np(), strerrordesc_np():
_GNU_SOURCE
strerror_r():
The XSI-compliant version is provided if:
(_POSIX_C_SOURCE >= 200112L) && ! _GNU_SOURCE
Otherwise, the GNU-specific version is provided.
- 메모리 할당: malloc(3)
MALLOC(3) Linux Programmer's Manual MALLOC(3)
NAME
malloc, free, calloc, realloc, reallocarray - allocate and free dynamic memory
SYNOPSIS
#include <stdlib.h>
void *malloc(size_t size);
void free(void *ptr);
void *calloc(size_t nmemb, size_t size);
void *realloc(void *ptr, size_t size);
void *reallocarray(void *ptr, size_t nmemb, size_t size);
Feature Test Macro Requirements for glibc (see feature_test_macros(7)):
reallocarray():
Since glibc 2.29:
_DEFAULT_SOURCE
Glibc 2.28 and earlier:
_GNU_SOURCE
- 메모리 할당과 초기화: calloc(3), 메모리 추가 할당: realloc(3), 메모리 해제: free(3)
MALLOC(3) Linux Programmer's Manual MALLOC(3)
NAME
malloc, free, calloc, realloc, reallocarray - allocate and free dynamic memory
SYNOPSIS
#include <stdlib.h>
void *malloc(size_t size);
void free(void *ptr);
void *calloc(size_t nmemb, size_t size);
void *realloc(void *ptr, size_t size);
void *reallocarray(void *ptr, size_t nmemb, size_t size);
Feature Test Macro Requirements for glibc (see feature_test_macros(7)):
reallocarray():
Since glibc 2.29:
_DEFAULT_SOURCE
Glibc 2.28 and earlier:
_GNU_SOURCE
- 옵션 처리: getopt(3)
GETOPT(1) User Commands GETOPT(1)
NAME
getopt - parse command options (enhanced)
SYNOPSIS
getopt optstring parameters getopt [options] [--] optstring parameters getopt [options] -o|--options optstring [options] [--] parameters
DESCRIPTION
getopt is used to break up (parse) options in command lines for easy parsing by shell procedures, and to check for valid options. It uses the GNU getopt(3) routines to do this.
The parameters getopt is called with can be divided into two parts: options which modify the way getopt will do the parsing (the options and the optstring in the SYNOPSIS), and the
parameters which are to be parsed (parameters in the SYNOPSIS). The second part will start at the first non-option parameter that is not an option argument, or after the first occurrence
of '--'. If no '-o' or '--options' option is found in the first part, the first parameter of the second part is used as the short options string.
If the environment variable GETOPT_COMPATIBLE is set, or if the first parameter is not an option (does not start with a '-', the first format in the SYNOPSIS), getopt will generate output
that is compatible with that of other versions of getopt(1). It will still do parameter shuffling and recognize optional arguments (see section COMPATIBILITY for more information).
Traditional implementations of getopt(1) are unable to cope with whitespace and other (shell-specific) special characters in arguments and non-option parameters. To solve this problem,
this implementation can generate quoted output which must once again be interpreted by the shell (usually by using the eval command). This has the effect of preserving those characters,
but you must call getopt in a way that is no longer compatible with other versions (the second or third format in the SYNOPSIS). To determine whether this enhanced version of getopt(1) is
installed, a special test option (-T) can be used.
반응형
'lesson > system programming' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 시스템 프로그래밍 05. 시스템 정보 (0) | 2024.08.22 |
|---|---|
| 시스템 프로그래밍 04. 파일 입출력 (0) | 2024.08.20 |
| 시스템 프로그래밍 03. 파일 다루기 (0) | 2024.01.25 |
| 시스템 프로그래밍 02. 디렉터리 다루기 (1) | 2024.01.25 |
| 시스템 프로그래밍 00. 시작 (2) | 2023.11.24 |


댓글